To those who have received the Commencement Notice (for importers) (Customs Form C No.5810)
To those who have received the Notice of Commencement of Verification Procedures (for importers) (Customs Form C No.5810)
Goods that infringe intellectual property are defined by law as “Cargo Prohibited for Import”.
If Customs detect goods suspected of infringing intellectual property in their inspection, they implement procedures to verify whether the goods fall under the category of goods infringing intellectual property. Such procedures are called “Verification Procedures”.
The Notice you have received from Customs is to inform you that the Verification Procedures have been commenced.
If it is determined that the goods fall under the category of goods that infringe intellectual property as a result of the Verification Procedures, the goods are not allowed to be imported.
1. Flow of Verification Procedures
“Commencement Notice” means the Notice of Commencement of Verification Procedures (for importers) (Customs Form C No.5810). The same applies hereinafter.
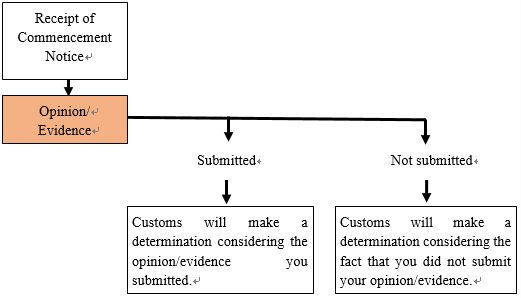
(Note) Whether or not you actively insist that the goods do not fall under the category of Cargo Prohibited for Import (do not infringe intellectual property) will affect the basis of determination by Customs. If you do not submit an opinion or evidence, such fact may be considered disadvantageous to you by Customs. It may be more likely to be determined that the goods infringe intellectual property.
2. Submission of written opinion and evidence
You may submit evidence and express your opinion on the fact that the goods do not fall under the category of Cargo Prohibited for Import (do not infringe intellectual property) by the deadline stated in “8. deadline for submitting evidence and expressing opinions” in the Commencement Notice.
If you are claiming that the goods do not fall under the category of Cargo Prohibited for Import, submit documents to prove such claim. In addition, if you are submitting any documents prepared in a language other than Japanese, please also submit a Japanese translation of such documents.
Please send (1) your written opinion stating the reasons why the goods do not fall under the category of Cargo Prohibited for Import (refer to below), and (2) evidence to clarify the reasons above (refer to below) by post to Customs at the address shown in [contact at] at the bottom of the Commencement Notice. (Do not enclose the Commencement Notice you received. Please keep it for yourself.)
Even if you submit an opinion and evidence, it does not necessarily mean that you will be able to import the goods. Please also be aware that the opinion and evidence submitted by you will be disclosed to the right holder (and the opinion and evidence submitted by the right holder will be disclosed to you).
Examples of goods which may be determined as not infringing intellectual property and may be imported as a result of the Verification Procedures are shown below.
【Goods which may be determined as not infringing intellectual property and may be imported】
(1) For patent rights, utility model rights, breeder’s rights or layout-designs of integrated circuits rights, goods that are not imported in the course of trade.
(2) For design rights and trademark rights, goods that are not imported in the course of trade, nor brought in from a foreign country to Japan in the course of trade by someone whom a person located in a foreign country arranged.
(3) For copyrights and neighboring rights, goods that are not imported for the purpose of distribution in Japan.
(Note) In determining whether or not it falls under “in the course of trade” in (1) and (2) above, or “purpose of distribution” in (3) above, we comprehensively consider various circumstances such as the purpose of importation, the occupation or business description of the importer and the sender, details of import transaction, the quantity and circumstances of goods to be imported, the record of previous importation, and the record of Verification Procedures commenced in the past, etc. Therefore, it is not simply determined “in the course of trade” or “for the purpose of distribution” based on whether the quantity of goods is one or more items. Even if the detected goods in question consist of one item, we will implement the Verification Procedures and decide whether the goods are infringing intellectual property based on submitted opinions and evidence, etc.
(4) Goods that are imported with the right holder’s consent.
(5) Goods that are parallel imported goods related to trademark rights, etc.
(6) Goods that do not infringe any intellectual property for any reasons other than above.
【Written Opinions】
Please enter the following items in Japanese in any format and submit it by post to Customs with evidence.
- The day you prepared the form
- Your name, address, telephone number, and occupation
- Commencement Notice Number (the number written in the upper right corner of the Notice; e.g. 123A-12345)
- Description of the goods, quantity
- Reasons for not infringing intellectual property
【Reasons for not infringing intellectual property】
Depending on the description of the intellectual property described in 5. of the Commencement Notice, the reasons for not infringing intellectual property may include the following:
(1) You are making a claim based on the reason that the goods are “not being imported in the course of trade, nor brought into Japan in the course of trade by someone whom a person located in a foreign country arranged”
Please specifically describe the purpose for importing the goods, your occupation, and details of the import transaction (e.g. who you purchased from, purchase price, payment method), as well as the name, occupation or business of the sender of the goods.
(Applicable: design rights, trademark rights)
(2) You are making a claim based on the reason that the goods are “not being imported in the course of trade”
Please specifically describe the purpose for importing the goods, your occupation, and details of the import transaction (e.g. who you purchased from, purchase price, payment method).
(Applicable: patent rights, utility model rights, breeder’s rights, layout-designs of integrated circuits rights)
(3) If you are making a claim based on the reason that the goods are “not imported for the purpose of distribution”
Please specifically describe the purpose for importing the goods, your occupation, and details of the import transaction (e.g. who you purchased from, purchase price, payment method).
(Applicable: copyrights, neighboring rights)
(4) You are making a claim based on the reason that “you obtained the right holder’s consent to import the goods”
Please specifically describe the consent you obtained from the right holder.
(Applicable: all types of intellectual rights)
(5) You are making a claim based on the reason that the goods are “legitimate parallel imported goods”
Please specifically describe that the goods satisfy the requirements for legitimate parallel import (see below).
(Applicable: patent rights, utility model rights, design rights, trademark rights)
(6) You are making a claim based on any other reason that the goods do “not infringe intellectual property”
Please specifically describe why the goods do not infringe intellectual property.
(Applicable: all types of intellectual rights)
【Evidence to clarify that the goods do not infringe intellectual property】
Please submit supporting evidence depending on the reason for your claim that the goods do not infringe intellectual property. If you claim that the goods do not infringe intellectual property but present no evidence, the grounds for your claim will be insufficient. In such case, the goods may be deemed as goods that infringe intellectual property.
Depending on the reason for the claim, evidence to clarify that the goods do not infringe intellectual property may include the following (a copied document is acceptable):
(1) You are making a claim based on the reason that the goods are “not being imported in the course of trade, nor brought into Japan in the course of trade by someone whom a person located in a foreign country arranged”
(a) E-mail or letters exchanged between you and the sender of the goods
(b) Documents indicating your occupation and the occupation of the sender of the goods
(c) Documents indicating the purpose or intended use of the imported goods
(d) Identification documents of you and the sender of the goods
(2) You are making a claim based on the reason that the goods are “not being imported in the course of trade”
(a) Documents indicating your occupation
(b) Documents indicating the purpose or intended use of the imported goods
(c) Your identification document
(3) If you are making a claim based on the reason that the goods are “not imported for the purpose of distribution”
(a) Documents indicating your occupation
(b) Documents indicating the purpose or intended use of the imported goods
(c) Your identification document
(4) You are making a claim based on the reason that “you obtained the right holder’s consent to import the goods”
- Document of the right holder’s consent
(5) You are making a claim based on the reason that the goods are “legitimate parallel imported goods”
- Documents indicating that the goods are legitimate parallel imported goods (see below)
(6) You are making a claim based on any other reason that the goods do “not infringe intellectual property”
- Documents indicating that the goods do not infringe intellectual property
【Legitimate parallel import】
(1) Parallel imported goods related to trademark rights
Even if the importer of the goods is not the trademark right holder, goods that are the same as designated products of a trademark right in Japan and thus having the same trademark as such registered trademark may be treated and imported as legitimate parallel import, only if you demonstrate that all of the items (a) through (c) below are satisfied.
(a) The trademark is lawfully attached by the trademark right holder in a foreign country or by a person who is licensed by the right holder
(b) The trademark indicates the same source of origin as the registered trademark in Japan, due to the fact that the trademark right holder in the foreign country and trademark holder in Japan are the same person or have a relationship that can be regarded as the same person in legal or economic aspect.
(c) The trademark right holder registered in Japan is in a position that can control directly or indirectly the quality of the goods in question, and it can be regarded that there is no substantial difference in the quality guaranteed by the registered trademark between the goods in question and the goods to which the registered trademark is attached by the right holder in Japan.
(2) Parallel imported goods related to patent rights
(A) If a patented product that is lawfully distributed outside of Japan by a registered patent right holder in Japan or by a person who can be regarded as the same (hereafter referred to as “patent holder, etc.”) is being imported by someone other than the patent holder, etc. or a person who is authorized to import the product, the product may be treated and imported as legitimate parallel import, only if you prove that the product does not fall under either item (a) or (b) below.
(a) The importer is a person to whom the product is transferred from the patent holder, etc., and there is an agreement between the patent holder, etc. and the transferee to exclude Japan from the area of sale or use of the product.
(b) The importer is a third party to whom the patented product is transferred from a transferee, and become a subsequent transferee, and there is an agreement between the patent holder, etc. and the transferee to exclude Japan from the area of sale or use of the product, and information on such exclusion is clearly displayed on the product
(B) In (A) above, a material for confirming that there is an agreement between the patent holder, etc. and the transferee to exclude Japan from the area of sale or the area of use of the product, means a contract or a similar document that confirms that there is such an agreement.
(C) In (A) (b) above, “information on such exclusion is clearly displayed on the product” means that at the time of transaction of the product, the main body or packaging of the product is imprinted, printed, attached with a sticker or hang tag, etc., indicating that Japan is excluded from the area of sale or use of the product, so that it can be easily recognized with ordinary attention. In addition, it has to be the case where it can be confirmed at the time of import that such indication was displayed at the time of the transaction of the product.
(3) Parallel imported goods related to utility model rights and design rights
The same concept is applied as above-mentioned (2) related to patent rights.
3. Notification of result of Verification Procedures
Based on the written opinion and evidence submitted by both you and the right holder, Customs determines whether the goods are infringing intellectual property or not, and notifies you of the result in writing.
You may not import the goods if it is determined that the goods fall under the category of goods that infringe intellectual property. You may import the goods if it is determined that the goods do not fall under the category of goods that infringe intellectual property.
4. Voluntary actions
Until Customs confiscates the goods, you may take “voluntary actions” as follows:
(1) Disposal or destruction
In the presence of Customs officials, you may dispose of or destroy the goods or ask a customs broker or international courier to do so on your behalf.
(2) Amendment of the goods such as by removing the parts that infringe or may infringe intellectual property
You may make amendment to the goods such as by removing the parts that infringe or may infringe intellectual property (amendment that can be easily undone is not acceptable), or ask a customs broker or international courier to do so on your behalf.
If the amended goods are confirmed as not infringing intellectual property, the goods may be imported.
However, the removed parts (marks, etc.) are not allowed to be imported.
(3) Reshipment
If you obtain export approval under the export control order, the goods may be reshipped (returned to a foreign country). However, the consent of the right holder is required to obtain such export approval.
If it is determined that the goods infringe trademark rights, copyrights, or neighboring rights, such export approval will not be granted.
(4) Consent of the right holder
If you obtain the written consent of the right holder to import the goods, and submit it to Customs at the address shown in [contact at] in the Commencement Notice, you may import the goods.
(5) Voluntary abandonment
You can waive your ownership of the goods by filling out the Declaration for Abandonment of Articles (Customs Form C No.5380) and submitting it to Customs at the address shown in [contact at] in the Commencement Notice.
If you have any questions about these procedures, please contact us at [contact at] in the Commencement Notice.
Verification Procedures
- Overview
- Sample Examination
- Deposit related to an Aplication for Import Suspension
- Seeking the opinion of the Commissioner of the Japan Patent Office
- Seeking the opinion of the Minister of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries
- Seeking the opinion of the Minister of Economy, Trade and Industry
- Requesting for discontinuance of the Verification Procedures



![Customs Channel[YouTube]](/mizugiwa/chiteki/english/common/img/banner-youtube.jpg)

