DNA Analysis(Determining the species of tuna)
DNA is the acronym for desoxyribonucleic acid, a macromolecule serving as an entity of genetic information in almost all living things. DNA's basic structure is a double helix where adenine (A) is paired with thymine (T) and guanine (G) is paired with cytosine (C) (base pairs) to form complementary double strands.
Using DNA to determine species
There are several methods of using DNA to determine a species. For example, a method of species determination by pattern recognition (identifying a species by comparing a sample with an existing database) is introduced here.
[ Let's see if we can determine a species. ]

1. Sample a piece of tuna.
2. Extract DNA from the piece.

3. Amplify a specific part of the DNA by the PCR method.

4. Use a restriction enzyme to cut the amplified DNA.

5.Separate each piece of DNA split into four parts by the electrophoresis method to recognize the pattern.
[ Let's look at the pattern. ]
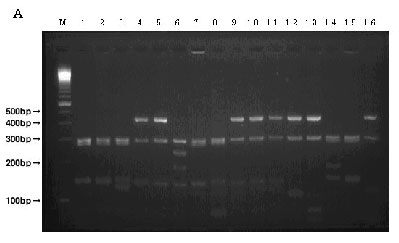
Electrophoretic image of a piece of tuna DNA using the AluI enzyme
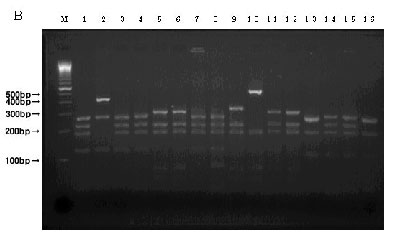
Electrophoretic image of a piece of tuna DNA using the MseI enzyme
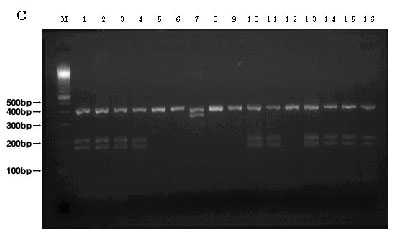
Electrophoretic image of a piece of tuna DNA using the TspEI enzyme
| Lanes 1 ~ 4: | Yellowfin tuna (Type1 ~ 4) |
| Lanes 5 ~ 12: | Bigeye tuna (Type1 ~ 8) |
| Lane 13: | Pacific northern bluefin tuna |
| Lane 14: | Atlantic northern bluefin tuna |
| Lane 15: | Southern bluefin tuna |
| Lane 16: | Albacore |
| M is a molecular marker, 100bp DNA Ladder | |
- Electron Microscope(Aluminum oxide or artificial corundum?)
- DNA Analysis(Determining the species of tuna)
- Textile Analysis(Natural or chemical fiber?)
- Comonomer unit wt% Measurement (Copolymer or not?)
- Salt Analysis(Checking the elements in salt)
- Oil Analysis(What are the differences between gasoline, kerosene, and light oil?)
- Rubber Test(Plastic or synthetic rubber?)
![]()
Major Analytical Equipment: Introduction of equipment and devices used for analyses
