Requested Analysis -Analysis Requested by the WCO-
A customs classification problem occurs if the category of a traded item differs between countries. If the two countries have different points of view regarding the classification, the World Customs Organization (WCO) requests analysis of the item by a reliable analytical organization outside the jurisdiction of the countries involved in the dispute to determine the classifications of the item in question. There are only a few organizations to which the WCO requests analysis, and Central Customs Laboratory (CCL) in Japan is one of them. When the CCL receives an analysis request from the WCO, the CCL examines the controversial items with a high degree of precision. The CCL then identifies the composition of the item from an objective and impartial point of view and reports the result to the WCO.
*Click on the graphic to see a larger one.
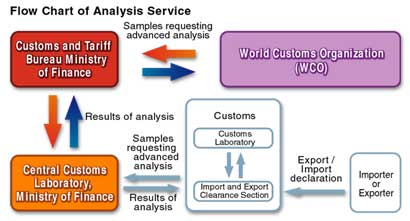
Flow Chart of Analysis Service
The Role of WCO
International trade is an important factor that drives the global economy. However, disunity and complexity in the customs systems of different countries must be an obstacle to international trade. An international organization was established in 1952 for the purpose of unifying and reconciling the customs systems of different countries and contributing to the development of international trade by providing technical cooperation to each country. This is The World Customs Organization (WCO: standard nomenclature is Customs Co-operation Council). With headquarters located in Brussels, Belgium, and the WCO has a total membership of 159 countries and regions (as of February 2002).
Globally Unified Classification Commodities (HS Convention)
To standardize the classifications of products being traded worldwide, in 1988, the WCO brought the "International Convention on the Harmonized Commodity Description and Coding System" (the HS Convention) into effect. The HS Convention is designed to cover all of the products that comprise world trade. Now, more than 98% of products being traded worldwide is classified in accordance with the HS Convention. Japan compiled a tariff list in accordance with this convention, and began applying the list on January 1, 1988.
![]()
Fruit Pulp Juice
Naturally, there is a wide variety of juices, including straight liquid types of squeezed oranges, grapefruits, apples, etc., slightly thicker types like tomato juice, and juices such as banana, mango and guava, with a high pulp content. The amount of fruit solids and pulp in these juices is measured to determine whether they should be classified as juices pr pulp products.
Iron Oxide
It may be different to think of the iron rust that you see so often as a product. It becomes a full-fledged product, though, when it serves as an ingredient for reddish-brown pigments. Some iron oxide is used for this purpose. Its purity is measured to determine whether it is simply the inorganic compound form of iron oxide, or whether it is a blended ingredient for pigments.
Dried Fruit
Even though different types of dried fruit may look the same, their classification changes depending on how they were made: simply dried, soaked in a syrup then dried, boiled in a syrup the dried, etc. The proper classification is determined by analyzing the fruit to determine whether its sweetness is due to its natural sugar content, or whether, and how. sugar has been added.
Requested Analysis
Research and Development
Technical Guidance
